RVC makes breakthrough in treatment of Alabama rot
Researchers at the Royal Veterinary College’s (RVC) Queen Mother Hospital for Animals (QMHA) have made a ground-breaking discovery in the treatment of Alabama rot, a deadly disease which affects dogs.
Alabama rot, properly known as Cutaneous and Renal Glomerular Vasculopathy (CRGV) first emerged in Alabama in the 1980s, giving it the nickname ‘Alabama Rot’. The lack of understanding on how it spreads or can be stopped has led to high fatality rates for dogs who develop it. The reason for its sudden appearance in the UK six years ago is still unknown.
It causes small clots in blood vessels, which eventually result in skin ulcers, tissue damage, and kidney failure in many cases. Many theories have been put forwards about the cause; ranging from E. coli-produced toxins to parasites and bacteria. However, without knowing the exact source it has been difficult for researchers to develop a cure.
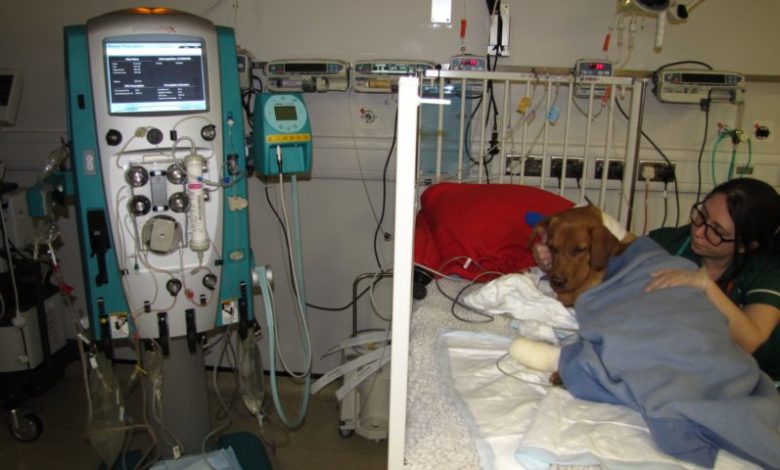
The new treatment considered to be a breakthrough is the Therapeutic Plasma Exchange (TPE) or ‘plasmapheresis ‘and is being offered by QMHA. This method involves filtering all the patient’s blood so that toxic substances, including whatever causes CRGV, are removed. Once filtered, the blood is returned to the patient.
Its development was made possible by the discovery of the similarities between Alabama Rot in dogs and thrombotic microangiopathy in humans, which is also treated with plasma exchange.
The QMHA academics reported that two out of six dogs who underwent plasmapheresis made a full recovery. The full findings of the research have been published in Frontiers in Veterinary Science.
Dr Stefano Cortellini, an author of the study and Lecturer in Emergency and Critical Care at the RVC, said: “Despite the fact that only a third of dogs treated with TPE recovered from their disease, this is the first time that dogs so severely affected by CRGV have been reported to survive and so we remain optimistic that TPE may play an important role in the treatment of this deadly disease.”